Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Earlier, Electric vehicle was not in use we depended on fossil fuels for the fulfillment of daily life requirements. Fossil fuels are Coal, Petroleum, and Natural gas, which are present in solid, liquid, and gaseous form, respectively. There are certain drawbacks with them; these are carbon rich, increase CO2 levels, which causes global warming globally and they are non-renewable resources; therefore, it will be problematic in the future when it will become consumed. Along with that it also causes major impact on environment through air pollution, oil spills, and land degradation, etc.

Therefore, to eradicate this problem, we can use alternative options of environment friendly and renewable energy sources such as Solar energy, Wind energy, Hydropower, and Bioenergy etc. Our government also promotes to use of renewable energy sources and has started various schemes in such areas.

Nowadays, one of the fastest-growing sectors is electric vehicles (EVs). It can reduce the dependency on fossil fuels in daily life. EVs’ modern revolution started from the early 19th century, but in the 20th century especially after 2015th, it caught a boom because many countries plan to phase out fossil fuel cars by 2030 to 2040 to achieve climate goals. Therefore, the EV option increases rapidly, but there was a major challenge in making highly efficient, fast charging batteries. To achieve its high efficiency, three key components play it’s major role-
3 key components of a battery
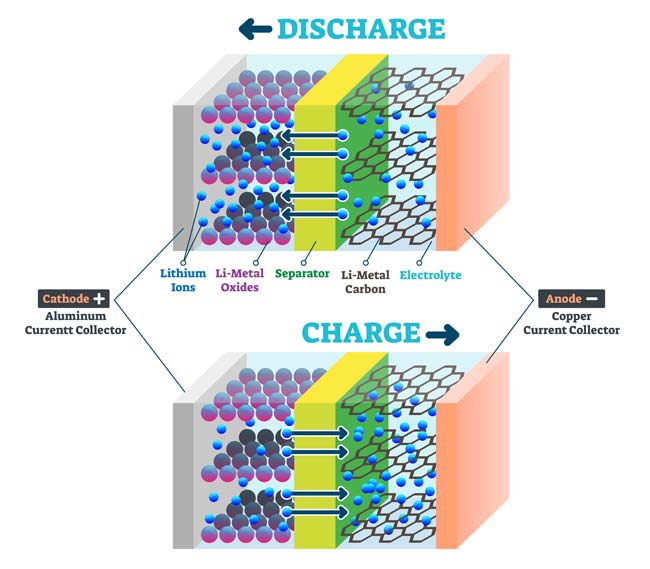
1. Anode (-)
| Releases electrons during discharge, usually
|
2. Cathode (+) | Receives electrons during discharge, made of |
3. Electrolyte
| Moves lithium ions between anode and cathode, exists in Liquid, |
High Efficiency Batteries
Highly efficient batteries have several characteristic features. Here can easily understand the advanced features of highly efficient batteries by differentiating them from conventional batteries-
| Feature | Conventional Battery | High-Efficiency |
Type | Lead-acid, older lithium-ion | Advanced lithium-ion (e.g., NMC, LFP), |
Energy Density | Low to moderate | High (more energy stored per kg) |
Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
Charging Speed | Slow to moderate | Fast charging (80% in 30 min or less) |
Lifespan (charge cycles) | 300–1000 cycles | 2000–5000+ cycles |
Efficiency (charge–discharge) | ~80% | 90–98% |
Temperature Sensitivity | Performs poorly in extreme weather | Better thermal control and performance |
Safety | Can overheat or leak (lead-acid) | Advanced safer (LFP, Solid-state) |
Cost | Cheaper | Costly |
Environmental Impact | More pollution, harder to recycle | Less toxic, increasingly recyclable |
Use Case | Common Battery Type |
Old Cars | Lead-acid |
Basic Electric Vehicle | Standard lithium-ion |
Modern Electric vehicle | NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt), LFP (Lithium |
Future Electric Vehicle | Solid-state batteries |
Type of modern batteries with key components:
Battery Type | Anode | Cathode | Electrolyte |
LFP | Graphite | Lithium Iron Phosphate | Liquid Lithium Salt |
NMC | Graphite | Nickel Manganese Cobalt | Liquid Lithium Salt |
Solid-State | Lithium metal | Varies (e.g. LFP, NMC) | Solid ceramic/polymer |
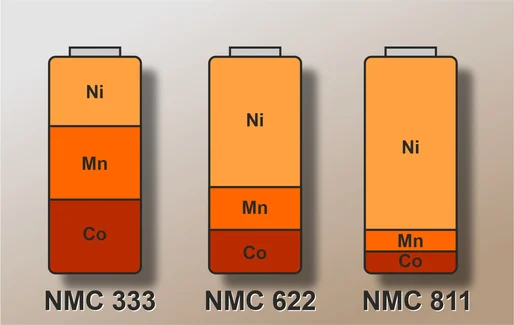
High-Nickel NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt):
These cathodes offer high voltage and capacity, supporting rapid charge and discharge cycle. It’s costly due to usage of cobalt and nickel. There are several variants are designed based on their chemistry, such as NMC 333, 622, and 811.
LFP ( Lithium Iron Phospate)
It is also an high efficient, more safer and having less energy density than NMC batteries. Due to their lower prize it’s highly adopted in affordable EVs.

Solid state batteries:
It is future of energy storage to make more efficient EVs. It can store more energy in smaller size because Anode – Electrolyte – Cathode ( all solid). Due to their characteristic features it is more safer ( non– inflammable) and efficiently works at extreme temperatures also.

Batteries Used in Affordable Electric Vehicle
Affordable electric vehicles (EVs), especially in markets like India, China, and Southeast Asia, commonly use LFP batteries (Lithium Iron Phosphate) due to their balance of safety, cost, and durability.
Region | Examples |
India | Tata Nexon EV, Ola S1 Pro, MG Comet EV |
China | BYD Dolphin, Wuling Mini EV |
Global | Tesla Model 3 & Model Y (base |
https://www.tesla.com/model3 https://ev.tatamotors.com/nexon/ev.html https://www.olaelectric.com/




Nice information sir👍
Thank you 🙏
“Great post! Battery upgrades are really driving the EV future.”👍
Thank you for your appreciation 🙏