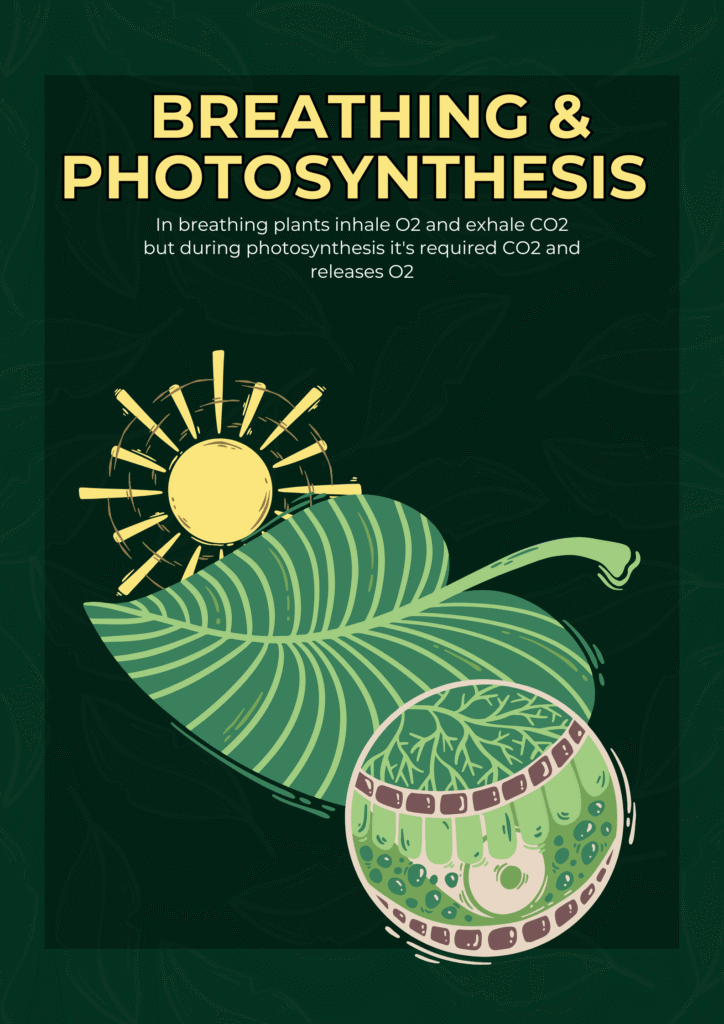
We all know about photosynthesis, that is the process by which plants make their food and releases O2 but By seeing plants question arises in our mind that “Do plants breathe” ?
Like animals plants also do respiration but intresting thing is that animals have lungs, a respiratory system to do respiration but it’s not found in plants. So the question arises that how plants do respiration?
The simple answer is that plants have few specialized epidermal cells that help them to do it.
eg. 1. Stomata, 2. Lenticel, 3. Root hairs
Contents
Toggle1. Stamata
It’s an simple structure of modified epidermal cells of leaves, made up of guard cells. These two guard cells form an stoma in leaf epidermal portion mostly fg pun on lower or abaxial side of leaf. These specialized cells having chloroplast, helps in photosynthesis. These two forms pore on plants leaf which is involved in gaseous exchange between plants leaves and surrounding environment.
Stomata act as leaf mouth perform major role during respiration, photosynthesis, and transpiration. During respiration inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, during photosynthesis inhale carbon dioxide and exhale oxygen and during transpiration it’s releases water vapour.
2. Lenticel
These are specialized pore found in plants stem and involved in gaseous exchange to help respiration in mature plants tissues. Lenticels are small, spongy openings present on the stems, twigs, fruits, and sometimes roots of plants. They play an important role in plant respiration (breathing). Here’s how they help:
Gas Exchange:
Lenticels allow oxygen (O₂) from the atmosphere to diffuse into the internal tissues of the plant, especially the living cells in the stem and root cortex.
Release of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
They also provide a passage for CO₂ and other gases produced during cellular respiration to move out.
Bypass for Bark:
Since the outer bark of woody plants is thick and impermeable, lenticels act as pores that bypass this barrier to maintain gaseous exchange.
Continuous Respiration:
Unlike stomata (which mostly function in leaves and can close), lenticels usually remain open, ensuring continuous respiration even at night and in woody parts.
Simply, we can say lenticels are like tiny breathing pores in the stem and fruits of plants. They help plants “inhale” oxygen and “exhale” carbon dioxide, especially in places where stomata are absent.
3. Root hairs
These are epidermal modification of roots plays an important role in respiration of root cells along with absorption. Because roots also required oxygen for their growth and living characteristics. Root hairs absorb oxygen from soil air spaces and carry out cellular respiration, generating ATP needed for active nutrient uptake and maintaining root function. Poor oxygen availability in soil limits root hair respiration, affecting plant health.

Very informative and helpful sir 👍