Contents
ToggleWhat is GLP-1
GLP-1 (Glucagon Like Peptide-1) is an naturally occurring hormone and also act as neurotransmitter. It’s secreted from small intestine and hind brain when we eat meal. In pancreas it helps to regulate blood sugar by increasing insulin and decreasing glucagon. GLP-1 also controls hunger and satiety centres in brain.
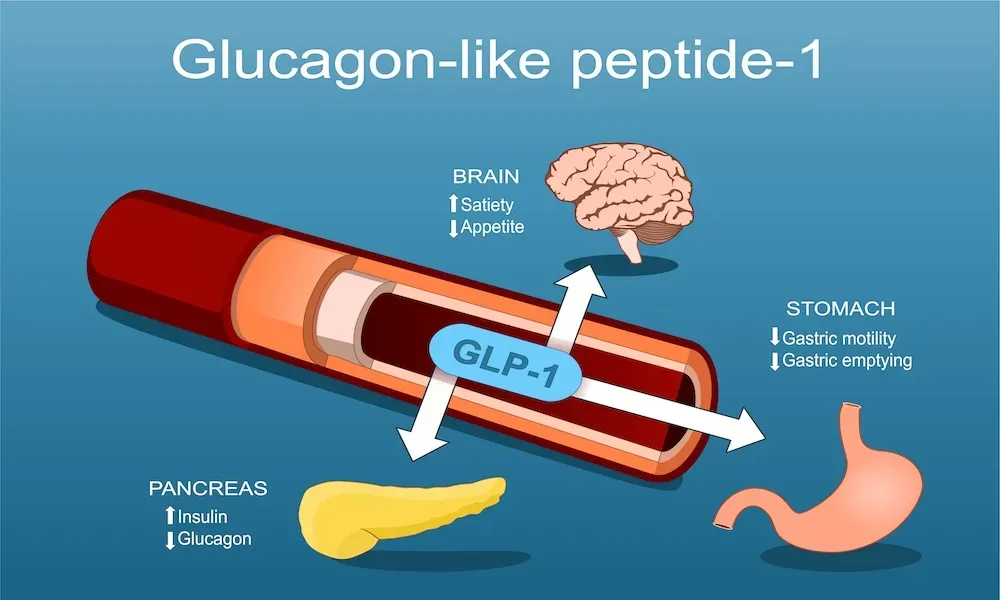
As we know GLP-1 is an hormone so their receptors are present in many organs in the body thereby provides beneficiary effects in many organs, such as the kidney, liver, and cardiovascular system. By controlling blood glucose levels through pancreas it can also control body weight.
How GLP-1 turned as drug
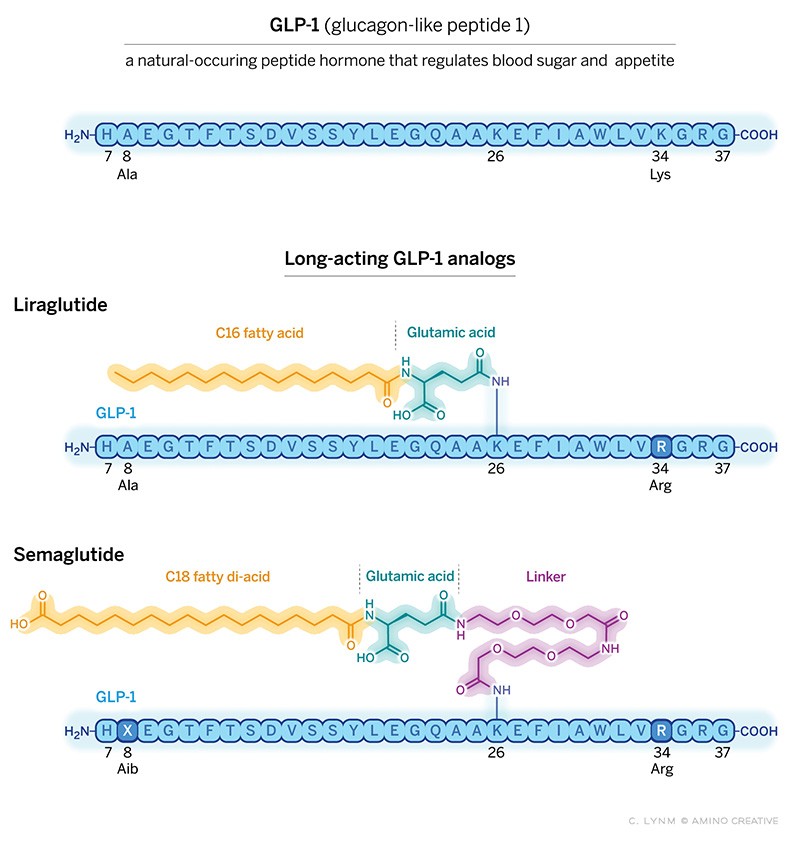
Semaglutide and liraglutide are injectible GLP-1 drugs work by mimicking the hormone GLP-1. The studies on GLP-1 started around early 1990s. But first time after introducing fatty acid with GLP-1, the research team of Lotte Bjerre Knudsen got registered first molecule for treatment of diabetes and obesity in 2009 and 2014 respectively.

Semaglutide is specifically designed for type 2 diabetes and also works in cardiovascular system therefore ultimately help in weight loss. By acting on cardiovascular system it can help in preventing heart attack and cardiac arrest.
The big “hurray” moment came when scientists finally solved the biggest problem with GLP-1: naturally it’s less stable (just about two minutes). And now they extend that up to 160 hours.
How GLP-1 drug become long lived
The natural GLP-1 is short lived because it’s chopped by metabolic enzymes known as DPP-4 and cleared by kidneys. By using fatty acid acylation they are able to develop long lived GLP-1. Fatty acid will allow the drug to bind to a natural protein called albumin. Albumin is a protein that plays crucial role in transporting various substances through out the body, including fatty acids. By attaching to albumin drug become protected from degradation.
A lot of things need to happen after we eat. Something needs to happen in our pancreas to help regulate blood sugar, something needs to happen in our brain to tell us to stop eating, and so on. GLP-1 works for just a few minutes, so after eat a meal and GLP-1 is secreted naturally, it gives immediate effect that last maybe 30 minutes.
By creating a GLP-1 analogue that works for 24 hours a day, whether it is given once daily or once weekly, we ensure that there is a sustained effect. So, if you have type diabetes, it helps you to regulate your blood sugar 24 hour a day. If you have obesity, it helps you to control your hunger and what you eat through out a day. If you are at risk of cardiovascular disease, it consistently helps dampen inflammation, and lowers blood pressure and some blood lipids.
GLP-1 acting organs
GLP-1 affects various organs. It works on pancreas to treat diabetes, on brain to help people feel more satiated, less hungry, and change how the eat, it works on gut to reduce inflammation, it also has effect on heart, kidneys, and other areas of brain. So, we can see it more as a multiorgan effect in beneficial ways. As we seen that it has ability to reduce inflammation by exploring that mechanisms scientists working on to treat Alzheimer.
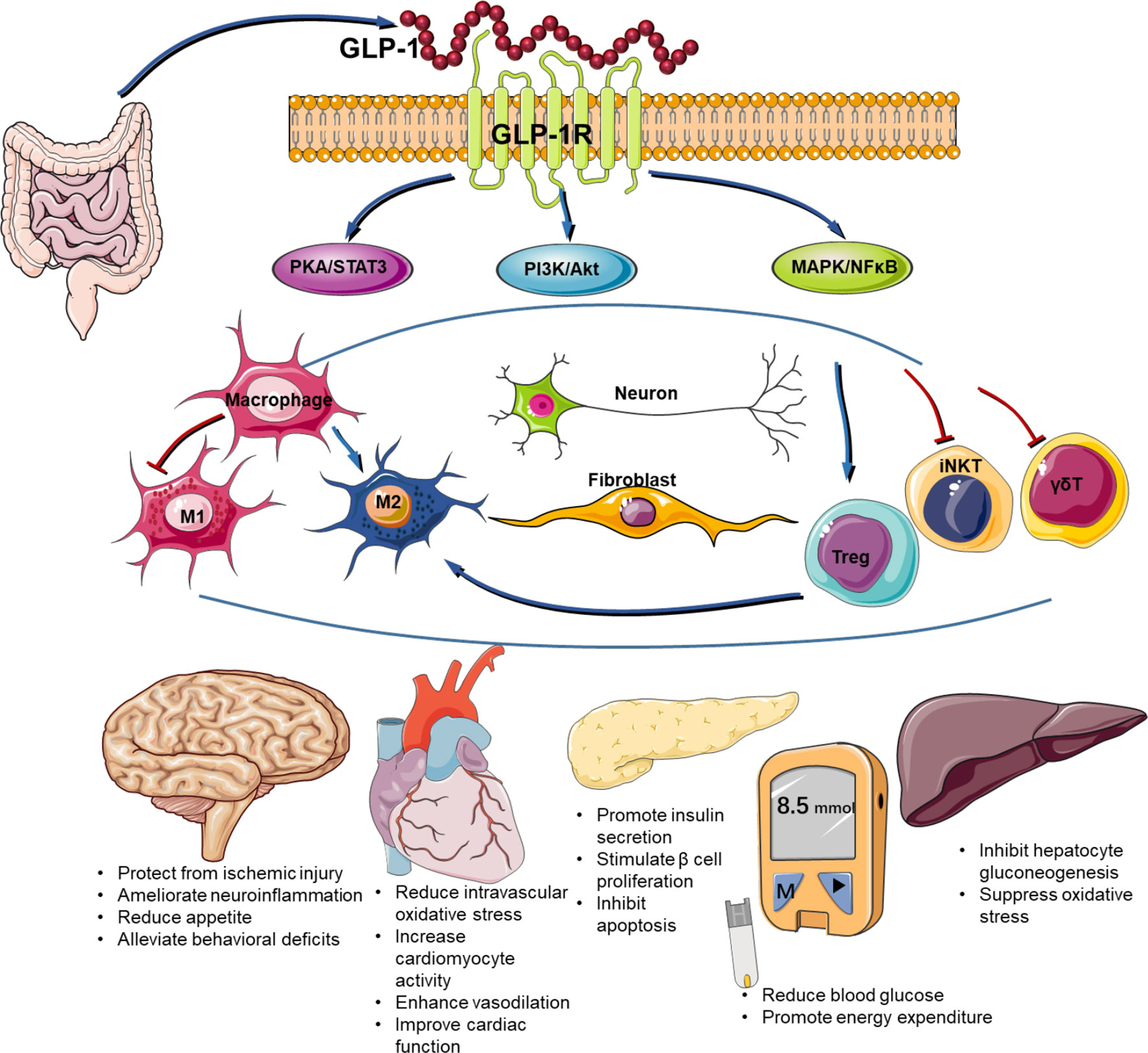
Side effects of GLP-1 drug
As we know side effects with all medicines. For all GLP-1 receptor agonists, the most common adverse effect on gastrointestinal, and usually mild to moderate and transient in nature.

This is very helful information